I. The potential risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by decreased bone density and degradation of the microstructure of bone tissue, resulting in increased bone fragility. Early screening is an important means to prevent serious complications such as fractures. As a non-invasive screening technique, ultrasound bone mineral density detection provides a reliable basis for bone health assessment.
II.The technical principle of ultrasonic bone density detection
By transmitting ultrasonic waves to bone, bone density parameters can be calculated by using the propagation speed and amplitude attenuation characteristics of sound waves in different density bone tissues. Its core advantages include:
1. High safety: no need for ionizing radiation, suitable for pregnant women, children and other special groups;
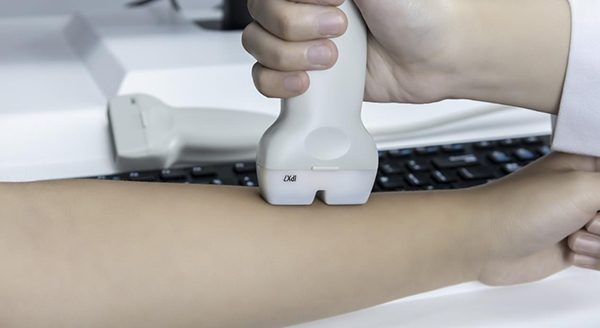
2. Convenient operation: the detection site is more than 1/3 of the tibia or the distal radius, and a single detection takes about 2 minutes;
3. Strong repeatability: short-term multiple detection can be achieved, which is convenient for dynamic observation of bone density changes.
III. Applicable population and detection significance
1. Reference to international guidelines for routine screening population:
WHO recommends routine screening for women over the age of 65;
The National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) : Women over 50 + men at high risk should be tested;
Chinese expert consensus: It is recommended that high-risk people over 40 years old be tested every 1-2 years.
2. Key monitoring groups:
Postmenopausal women (decreased estrogen levels lead to accelerated bone loss);
Long-term use of glucocorticoids or antiepileptic drugs;
Patients with metabolic diseases such as chronic kidney disease and hyperthyroidism.
3. Clinical application value:
Bone loss was found early (T-value -2.5 ~-1.0);
Quantify fracture risk (for every 1 standard deviation reduction in BMD, fracture risk increases by 1.5-2 times);
Evaluate the effectiveness of anti-osteoporosis treatments (such as calcium, vitamin D, or bisphosphonates).
IV. Clinical interpretation of test results
Ultrasound bone densitometers are standardized for evaluation with T-values and Z-values:
·T value: Comparison of peak bone mass in healthy young adults of the same sex (WHO standard)
·≥-1.0: indicates the normal range
·-2.5~-1.0: decreased bone mass
·≤-2.5: Osteoporosis
·Z value: average BMD compared with peers
·≥-1.0: normal bone mass
·≤-1.0: Abnormal bone mass should be combined with clinical analysis
V. Testing precautions
· Preparation: Wear loose clothing to expose the tibia or radius
· Special cases: Patients with severe arthritis or local malformations should inform the testing physician in advance
Regular ultrasound bone mineral density detection combined with scientific lifestyle intervention can effectively delay bone loss and reduce the risk of osteoporotic fracture. It is recommended to develop a testing plan according to the individual risk level to achieve full cycle management of bone health.
Post time: Mar-07-2025